Proprietorship Registration

What is Proprietorship Registration?
A sole proprietorship is a popular business structure in India ,where a single individual establishes and manages the business. It is an ideal Choice for those who want to start a business with limited investment. Typically ,this form of business does not require any formal registration.
A sole proprietorship business can be initiated either from a home or a premises ,requiring only a minimal investment. The sole proprietor/owner retains complete control over the business, assuming all responsibilities for losses and reaping all profits. While the proprietor can delegate tasks to employees, the ownership remains exclusively in their hands.
Various local businesses, Including Grocery stores, parlors, boutiques,retail stores,and more ,have the option to operate as a sole proprietorship. This business structure is also accessible for small traders and manufacturers.
Who can OPT for Sole Proprietorship?
The digital signature is issued by the certifying authority responsible for issuing certificates. Additionally, individuals authorized as signatories for manual documents are required to obtain a digital signature as per MCA21 regulations. This requirement applies to personnel such as directors, auditors, company secretaries, bank officials, and other authorized signatories.
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Less compliances: The sole proprietorship business can be effortlessly initiated by a single individual. The incorporation process involves minimal compliance requirements. Compared to a company or LLP, this business form is cost-effective, requiring relatively less initial investment.
- Control of the business: The sole proprietor Possesses full authority over the business and assumes responsibility for all its aspects. As the business is run by a single individual ,it enables the maintenance of confidentiality.
- Quick decision making: The Sole Proprietor holds Complete decision-making authority in the business. Being a single person ,decisions can be made swiftly and independently ,without the need for external consultations.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Unlimited liability: The sole proprietor carries unlimited liability ,meaning they are personally responsible for all busins transactions. In the event of any losses ,the sole proprietor must bear the entire burden using their personal assets.
- No perpetual succession: Sole proprietorship lacks perpetual succession, meaning if anything happens to the sole person managing the business, it can cease to exist. The business is vulnerable to closure at any given time.
- Difficult to raise funds: Due to the sole management by a single individual ,raising capital can be challenging for a sole proprietorship. The business relies solely on the investments made by the proprietor. Furthermore ,as the sole proprietorship does not possess a separate legal entity status apart from the owner ,obtaining funds from external sources becomes difficult ,particularly given the potential for the business to cease operations at any time.
Documents Required for Sole Proprietorship

Aadhaar Card

Pan Card

Registered Office Proof

Bank account
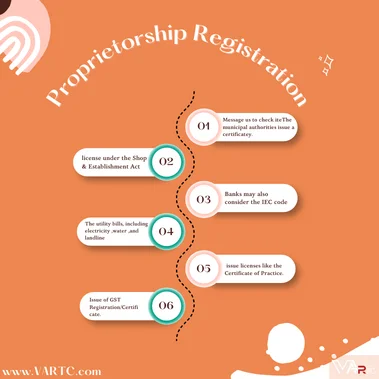
Checklist Items for a Sole Proprietorship Registration
- The municipal authorities issue a certificate/license under the Shop & Establishment Act.
- The Registering authorities ,such as the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, issue licenses like the Certificate of Practice.
- The registration/licensing document is issued in the name of the proprietary concern by either the Central Government or the State Government Authority/Department
- Banks may also consider the IEC code (Importer Exporter Code) issued by the office of the DGFT as a valid identity document for purposes like opening a bank account.
- The sole proprietor must duly complete and authenticate the online Income Tax return in their name, where the firm’s income is reflected. The return should be acknowledged by the Income Tax Authorities.
- The utility bills, including electricity ,water ,and landline telephone bills, should be issued in the name of the proprietary concern.
- Issue of GST Registration/Certificate.

Compliances Required For Sole Proprietorship Firm
Some of the compliances that apply to a sole proprietorship include the following:
- Income Tax Return Filing: The Owner of the Proprietorship business is responsible for Submitting their Personal Income tax return using Either form ITR-3 or ITR-4.
- Business Income: To Fulfill income tax obligations ,proprietorships are required to submit either form ITR-3 or ITR-4 ,as these forms Specifically allow for the declaration of business income.
- GST Return Filing: If a proprietorship is registered for GST ,it must file monthly or quarterly GST returns based on the chosen registration plan for the business.
- TDS Returns: If the Proprietorship has employees or spends a certain amount on goods and services ,tax must be deducted at source, and quarterly TDS returns need to be filed.

Timelines for Sole Proprietorship Registration
To establish a Sole Proprietorship, the following steps are necessary: opening a business bank account ,obtaining a Certificate of Registration under the Shop and Establishment Act from the relevant state ,and completing GST registration. The registration process typically takes around 10 days ,depending on departmental approval and responses from the respective authorities.
Registration of Sole Proprietorship
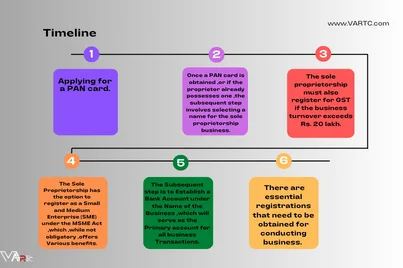
The procedure for incorporating a sole proprietorship firm is-
- Applying for a PAN card.
- Once a PAN card is obtained ,or if the proprietor already possesses one ,the subsequent step involves selecting a name for the sole proprietorship business.
- The Subsequent step is to Establish a Bank Account under the Name of the Business ,which will serve as the Primary account for all business Transactions.
- While no specific registration is mandatory for commencing a sole proprietorship firm, there are essential registrations that need to be obtained for conducting business. The basic registrations required by a sole proprietorship include:
- The proprietor must acquire the Registration Certificate under the respective state’s Shops and Establishment Act, corresponding to the location of the business.
- The sole proprietorship must also register for GST if the business turnover exceeds Rs. 20 lakh.
- The Sole Proprietorship has the option to register as a Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) under the MSME Act ,which ,while not obligatory ,offers Various benefits.
How VARTC Executes a Sole Proprietorship Registration Procedure?
Professional Guidance
Our team of experts provides professional guidance for various processes involved in registering your business as a sole proprietorship. We assist with the registration of service tax, sales tax, import/export code, and professional tax.
Vendor Relationship
Our team will connect you with reputable vendors who specialize in handling application bookings, keeping you informed about the status and progress. These vendors have extensive experience and expertise in managing local registrations.
15 Business Days
Our Team is Committed to Providing comprehensive assistance throughout the registration process ,which may take anywhere between 5 to 15 days ,depending on the Specific tasks required by the relevant authorities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
A- A proprietorship firm is a type of business structure where a single individual owns and manages the entire business. The proprietor is personally liable for all the debts and obligations of the firm. Proprietorship firms are easy to set up and operate, making them a popular choice for small businesses and startups in India.
A- There are mainly four types of proprietorship in India:
- Sole Proprietorship
- One Person Company (OPC)
- Registered Proprietorship
- Unregistered Proprietorship
Each type of proprietorship has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of business structure depends on the proprietor's needs, goals, and resources.
A- Proprietorship and firm are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference between the two. Proprietorship refers to a type of business structure where a single individual owns and manages the entire business, while a firm refers to a group of individuals who come together to carry out a business activity. In a firm, the ownership is shared among the partners, and the profits and losses are also shared among them. In contrast, in proprietorship, the proprietor has complete control over the business, and all the profits and losses belong to the proprietor alone.
A- No, there is no certificate of Incorporation given.
A- As the sole proprietorship and the proprietor are the same the individual has to just file the Income-tax returns and GST returns filing for the proprietorship firm.
A- No, there is no minimum requirement to start a sole proprietorship in India.
A- The sole proprietorships exist as long as the proprietor is alive and is desiring to run the business.
A- Yes, a sole proprietor is considered to be the same as the sole proprietor.
A- It generally differs from state to state as in Maharashtra a Shop and Act license is required and for West Bengal, the trade license is required.
A- The proprietor owns, controls, and manages the sole proprietorships. He has a complete hold over the proprietorship.
